Most Linux distributions that are installed using virtual machine software like VirtualBox or VMware are configured to skip the GRUB bootloader for a seamless user experience.
However, certain events might require you to access the GRUB menu, such as switching to an older kernel version, editing the kernel parameter, entering recovery mode, or resetting the password.
In this quick guide, I'll show you two different ways to access the GRUB menu of Debian, Ubuntu, Red Hat, or Fedora running on virtual machines.
Access the GRUB Menu in Virtual Machine
Most users might not need to access the GRUB menu regularly. For that purpose, you can use a temporary solution to access the GRUB menu without any configuration changes.
Method 1: Access the GRUB Menu in VM (One-Time Solution)
To access GRUB just once, simply boot your system and hold the shift key until the GRUB bootloader appears.
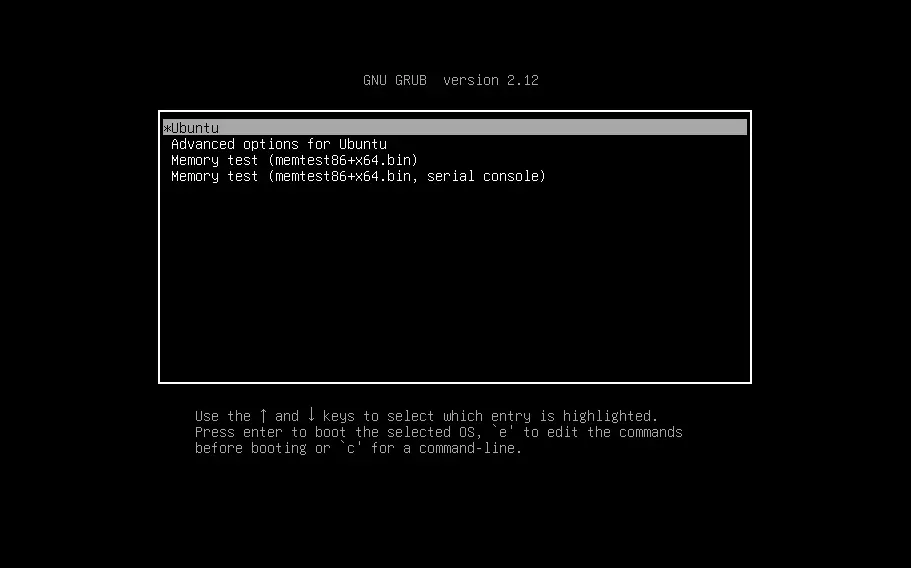
You'll have the GRUB without any time limit.
As you can see, it's straightforward to access GRUB on a Linux VM with a simple one-time shortcut key solution. However, this method only works for single boots. So, if you want a permanent solution, then check out the next method.
Method 2: Access the GRUB Menu in VM (Permanent Solution)
This method involves editing the GRUB config file in the command line, so if you need to access GRUB on a daily basis, you can follow this method. First, open your terminal and edit the GRUB config file using this command:
$ sudo nano /etc/default/grub
Then change the GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE parameter value to "menu", which will display the GRUB menu, and set the GRUB_TIMEOUT parameter value to "5", which will display the GRUB menu for only 5 seconds.
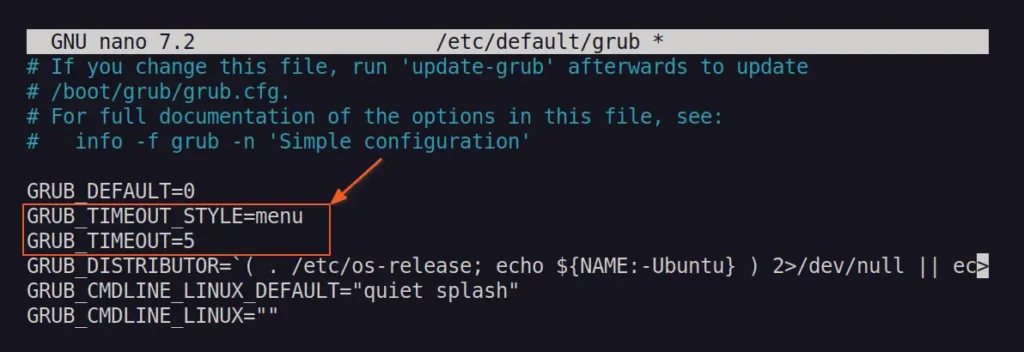
After editing, save and close the file.
Apply the new changes you made to the GRUB configuration file using this command:
$ sudo update-grub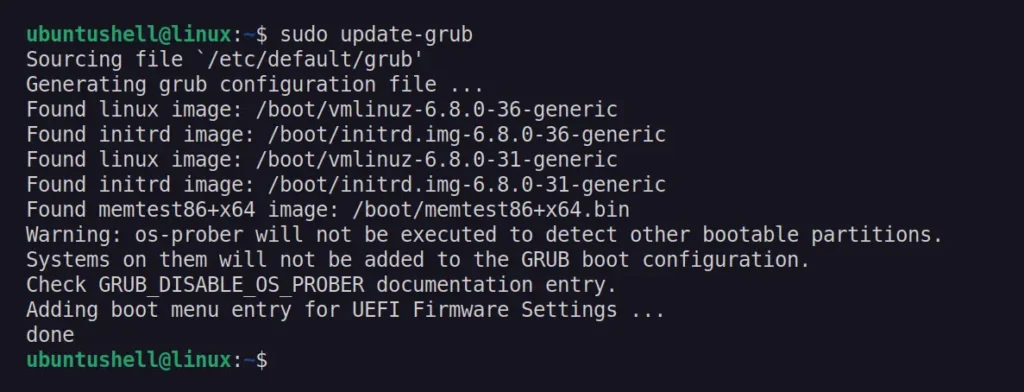
That's it. You can now reboot your system to check the GRUB menu.
Wrap Up
Today, you've learned how to display the GRUB menu on a Linux system running on a VM. The method described in this article is demonstrated on Ubuntu 24.04 but is applicable to all other Linux distributions.