Multiple Linux desktop environments (or "DEs") are available on the market, with popular ones being GNOME, KDE Plasma, and Xfce. Although each Linux distribution ships with a different desktop environment depending on different criteria.
For example, the most popular Linux distribution, Ubuntu, comes with GNOME, although different variants are available, such as Kubuntu (which comes with KDE) and Xubuntu (which comes with Xfce).
But if you have downloaded and installed Ubuntu from the official Ubuntu ISO file, then most likely you have GNOME installed on your system. However, if you want to try a different DE, you can either install new distros with your desired DE configured (not suggested) or simply install your desired DE from the default package manager.
Installing Different Desktop Environments on Ubuntu
If you're using the official Ubuntu distribution that runs on GNOME, then you can easily install other popular DEs from the default package manager. So, let's start with…
Install KDE Plasma on Ubuntu
If you're using Ubuntu with GNOME, then you don't need to remove it; you can easily install the KDE desktop on your current Ubuntu system and switch between the available desktop environments from the login screen.
There are different variants of the KDE package available, so you can install one of them according to your requirements.
- Install the complete KDE Plasma Desktop with both the complete package and the core KDE Plasma Desktop (the package size is around 1 GB).
- sudo apt install kde-full
- Install the standard KDE Plasma Desktop with a standard set of KDE apps such as Kate, Konqueror, KGet, KMail, Dolphin, etc. (the package size is around 273 MB).
- sudo apt install kde-standard
- Install the minimal KDE Plasma Desktop with a minimal set of KDE apps such as a browser, file manager, text editor, etc., suitable when you just want to give it a try (the package size is around 175 MB).
- sudo apt install kde-plasma-desktop
During installation, you will be prompted to configure "SDDM", i.e., Simple Desktop Display Manager, the Display Manager used by the KDE Desktop. Select "sddm" from the list and press Enter.
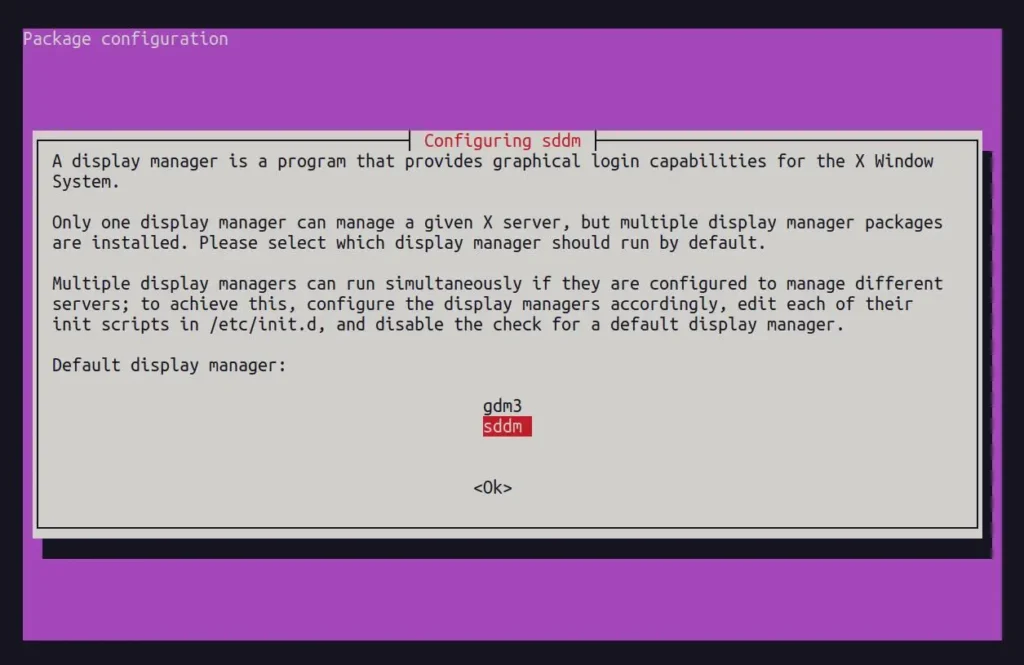
Once you've done it, it will configure the remaining packages. Then, you can reboot, choose KDE on the login screen (if required), and log in with your default credentials.
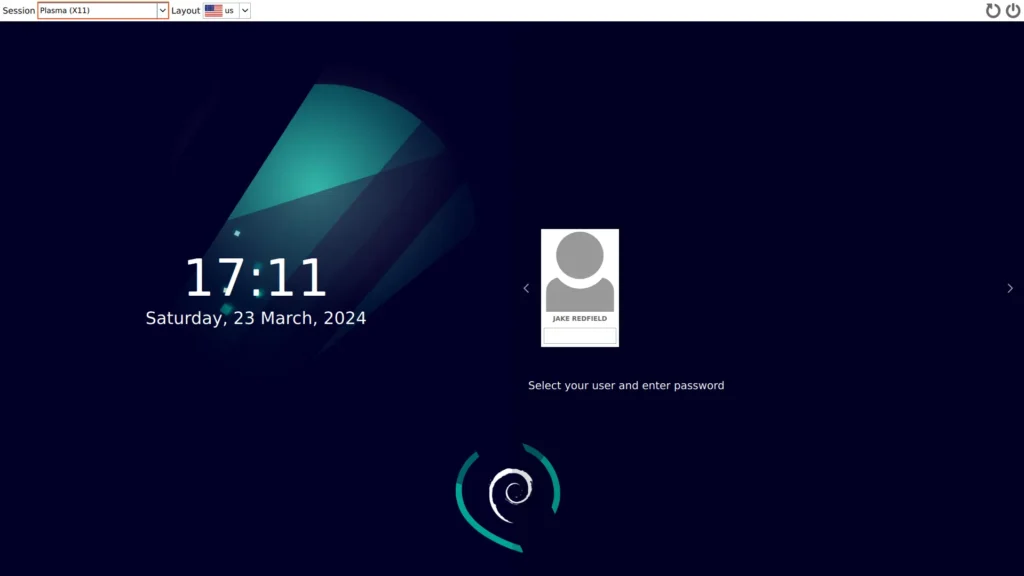
Here, you can start using KDE as your default desktop environment, and if you wish to switch to GNOME, select the GNOME session from the top left corner of the login screen.
Install Xfce on Ubuntu
There are two different ways to use Xfce on an Ubuntu system: either by installing the Xfce desktop (via the xfce4 package), or by installing the Xubuntu desktop (via the xubuntu-package package).
The difference between them is that Xfce Desktop comes with a basic package, so most of the applications that you use will be the same as your GNOME. While the Xubuntu desktop comes with its basic package, it also comes with a set of apps and a boot screen.
So, if you want to just test Xfce, then go with the Xfce desktop, but to experience Xfce fully (or, you can say, Xubuntu), go with the Xubuntu package.
- Install the Xfce desktop.
- sudo apt install xfce4
- Install the Xubuntu desktop.
- sudo apt install xubuntu-desktop
If the installation prompts you to select a display manager, you have the option to choose "gdm3" for Gnome or "lightdm" for Xfce. For now, I'll choose "gdm3".
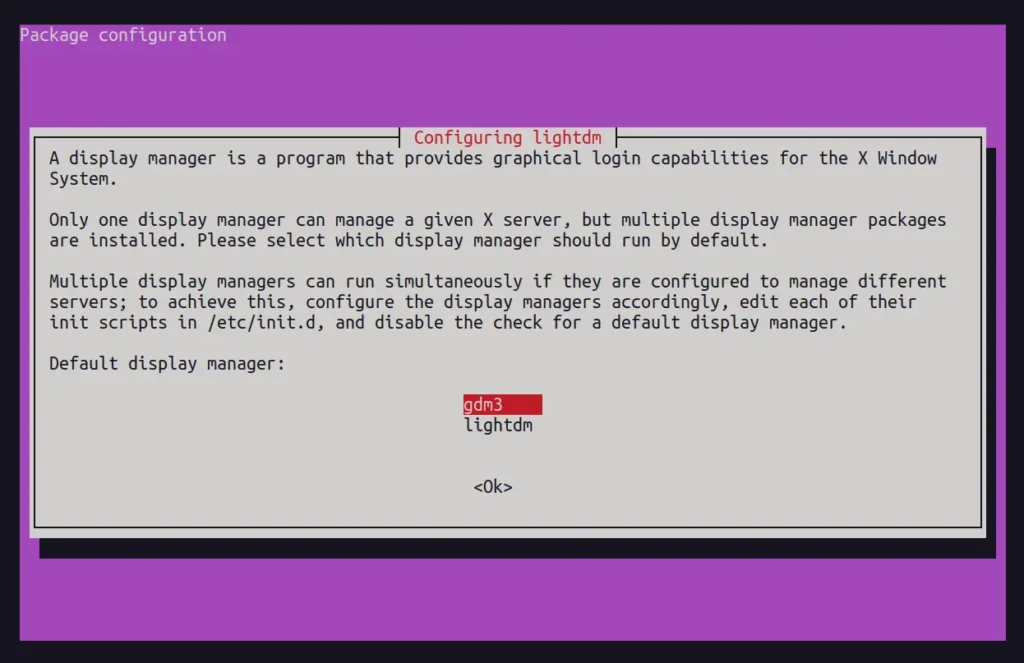
Once you've done that, it will configure the remaining packages. Then, you can reboot and choose "Xfce Session" or "Xubuntu Session" from the login screen.

Here, you can begin using Xfce as your default desktop environment, and if you desire to switch to GNOME, you can do so from the login screen.
Install LXQt on Ubuntu
LXQt is a lightweight yet feature-rich desktop environment for your Ubuntu system. So, if your system is running on low specs, you can prefer to use LXQt.
In Ubuntu, it can be installed in two different ways: either by installing it using the task-lxqt-desktop package, which will install the full LXQt, or by using the lxqt package, which will install the minimal server installation.
- Install the full LXQt desktop.
- sudo apt install task-lxqt-desktop
- Install the minimal LXQt desktop.
- sudo apt install lxqt
During installation, if you are asked to choose a display manager, you can select between "gdm3" (for Gnome) or "sddm" (for LXQt). For now, I'll choose "gdm3".
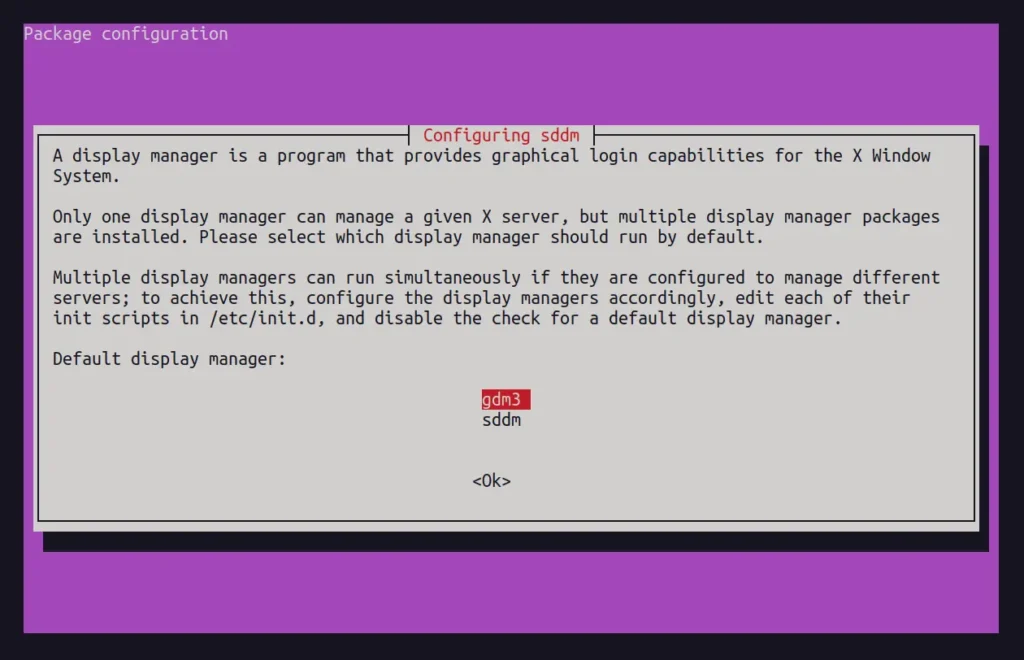
Once you've done that, it will configure the remaining packages. Then, you can reboot and choose "LXQt Desktop" from the login screen.

Here, you can begin using LXQt as your default desktop environment, and if you desire to switch to GNOME, you can do so from the login screen.
How to Remove the Installed Desktop Environment on Ubuntu
After installing your desired DE, if you want to revert to GNOME and remove the other installed DE, first ensure logging in with GNOME from the login screen.
Next, change the default display manager to "gdm3" (Gnome desktop manager) by executing the following command:
- sudo dpkg-reconfigure gdm3
Finally, follow one of the methods mentioned below based on the installed DE to remove it from your system.
For KDE Plasma
Execute one of the following commands based on the KDE variant you have installed:
- sudo apt --purge remove kde-full
- sudo apt --purge remove kde-standard
- sudo apt --purge remove kde-plasma-desktop
- After executing one of the above commands, make sure to remove all unused dependencies by running the following command:
- sudo apt autoremove
Once done, make sure to restart your system.
For Xfce
If you used the xfce4 package, use the following commands to remove Xfce:
- sudo apt purge xubuntu-icon-theme xfce4-*
- sudo apt autoremove
If you used xubuntu-desktop package to install Xfce, use the following command:
- sudo apt purge xubuntu-desktop xubuntu-icon-theme xfce4-*
- sudo apt purge plymouth-theme-xubuntu-logo plymouth-theme-xubuntu-text
- sudo apt autoremove
After completing the task, ensure that you restart your system.
For LXQt
To remove LXQt, simply execute the following command:
- sudo apt-get remove lxqt*
- sudo apt autoremove
Ensure to restart your system once you've finished.
If your GNOME DE is causing issues such as crashes or errors, ensure to reinstall it by executing the following command:
- sudo apt update && sudo apt install ubuntu-gnome-desktop
- sudo reboot
That's it! I hope you found this article useful and learned multiple ways to install different DEs on Ubuntu and then remove them if you didn't like them.