Blender is a free, open-source, cross-platform 3D graphics software providing tools for 3D modeling, animation, rendering, and more for 3D artists, animators, and game developers.
There are several ways to install it on Ubuntu; one common method is using the APT command, but this will install an older version. To get the latest version, you can use alternative methods such as a Snap, Flatpak, or Tarball file.
If you want to install it on Ubuntu, you can use the Snap method because the Snap package manager comes pre-installed; if you're using Fedora, you can use the Flatpak method, which comes pre-installed on those systems. However, you're free to use any method you prefer.
So, let's see how to install Blender on Ubuntu and other Linux distros using Snap, Flatpak, and the Tarball file method.
Method 1: Install Blender via Snap Package
The Snap is the easiest way to quickly install the latest version of Blender on Ubuntu, though it runs in a sandboxed environment. To begin the installation, simply open your terminal and run the following command to install the Blender Snap package:
$ sudo snap install blender --classic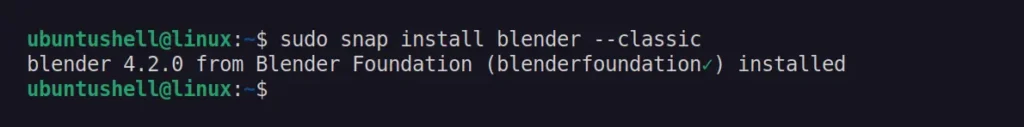
Once the installation is complete, you can launch the program from the application menu, and when an update is available, the Blender Snap package will automatically be updated in the background.
Method 2: Install Blender via Flatpak
Flatpak is another popular sandbox technology that is similar to Snap and comes pre-installed in some popular Linux distributions, such as Fedora. If you prefer Flatpak over Snap, you can use the following instructions to install the Blender Flatpak package:
First, open your terminal and install Flatpak using one of the appropriate commands:
# On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, etc.
$ sudo apt install flatpak
# On Red Hat, Fedora, AlmaLinux, etc.
$ sudo dnf install flatpakNext, run the following command to install the Blender Flatpak package:
$ flatpak install https://dl.flathub.org/repo/appstream/org.blender.Blender.flatpakref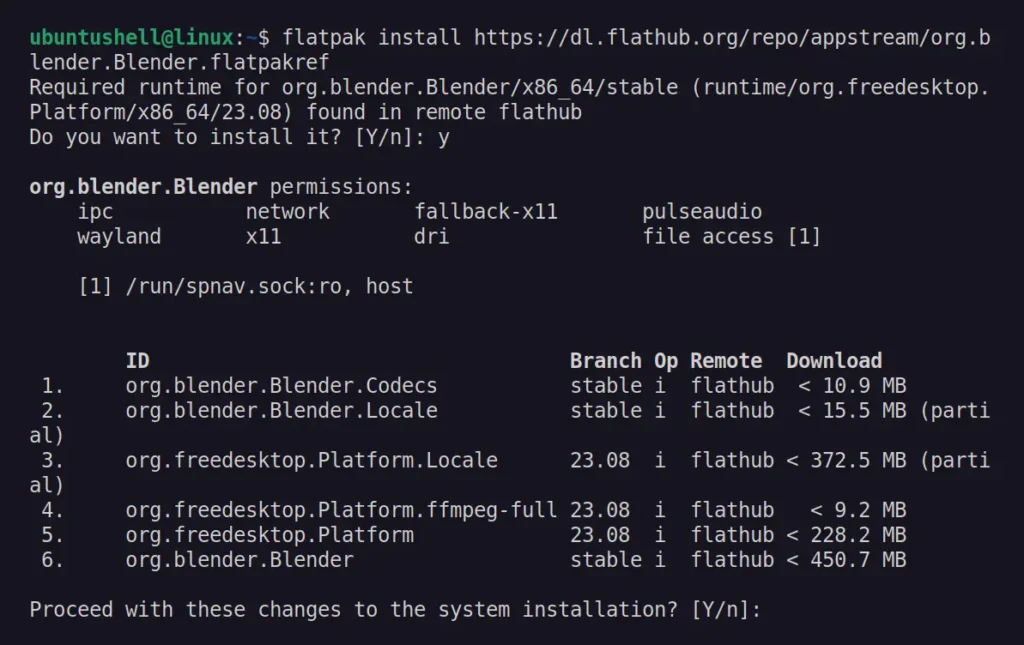
Once the installation is complete, you can launch it from the application menu, and like Snap, it will automatically update in the background when an update is available. However, if you prefer to manually perform the update, execute the flatpak update org.blender.Blender command.
Method 3: Install Blender via Tarball File
This method ensures you get the latest package without using sandbox technologies like the previous two, but it's not beginner-friendly, so follow this method to install Blender only if you have some experience with the Linux command line.
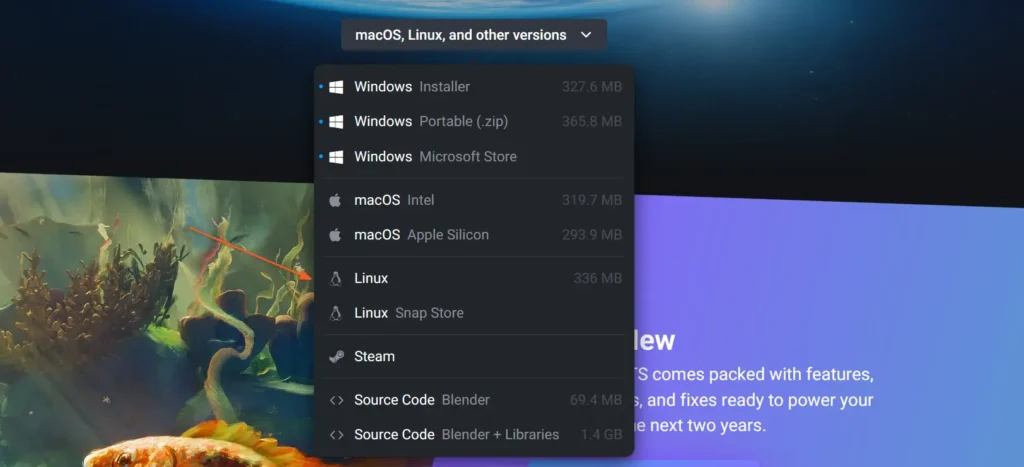
When you're ready, visit the official Blender download page and download the Tarball file for Linux, which will end with the ".tar.xz" extension.
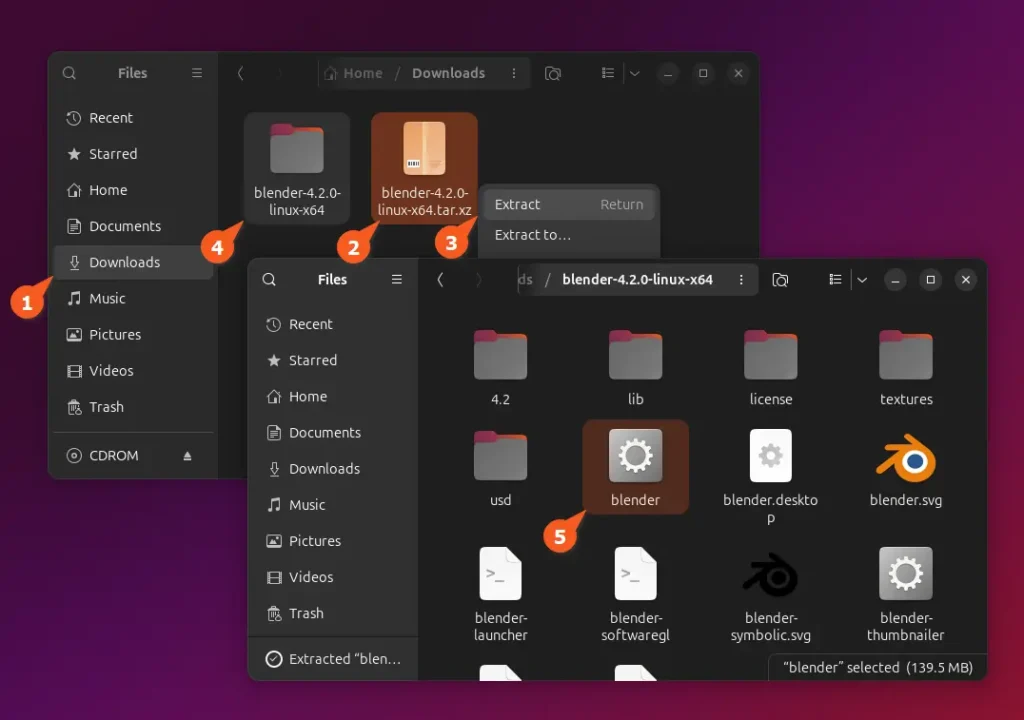
Once the download process is complete, you can launch the file explorer, navigate to the downloads directory, extract the Tarball file, enter the extracted directory, and double-click the blender executable file.
It launches Blender from the executable file; in the future, when an update is available, you will receive a notification to update to the latest release.
Uninstall Blender from Linux
To uninstall Blender installed via Snap or Flatpak, simply open your terminal and execute the appropriate command based on your installation method.
# On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, etc.
$ sudo snap remove blender
# On Red Hat, Fedora, AlmaLinux, etc.
$ flatpak uninstall org.blender.BlenderIf you are accessing Blender from a tarball file, simply remove the Blender directory.
Wrap Up
In this article, you’ve learned how to install Blender on Ubuntu and other Linux distros using different methods. I’ve tested it on nearly every Linux distribution, including the latest Ubuntu 24.04, and it works like a charm. If you have any questions, you can ask me in the comments section.